
Hydrogen sulfide dysregulates the immune response by suppressing central carbon metabolism to promote tuberculosis | PNAS

Hydrogen sulfide dysregulates the immune response by suppressing central carbon metabolism to promote tuberculosis | PNAS

Transcriptomic similarities and differences in host response between SARS-CoV-2 and other viral infections - ScienceDirect

High titers and low fucosylation of early human anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG promote inflammation by alveolar macrophages
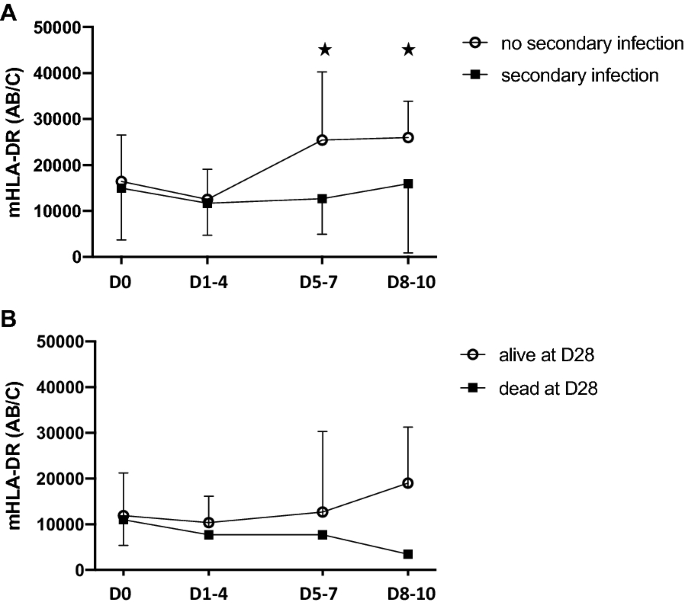
Myeloid phenotypes in severe COVID-19 predict secondary infection and mortality: a pilot study | Annals of Intensive Care | Full Text
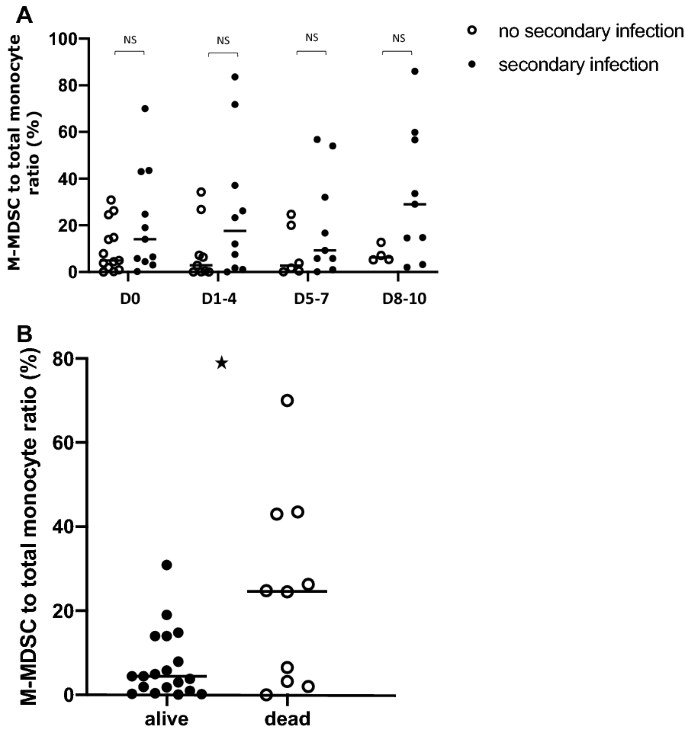
Myeloid phenotypes in severe COVID-19 predict secondary infection and mortality: a pilot study | Annals of Intensive Care | Full Text

Transcriptomic similarities and differences in host response between SARS-CoV-2 and other viral infections - ScienceDirect

Transcriptomic similarities and differences in host response between SARS-CoV-2 and other viral infections - ScienceDirect

High titers and low fucosylation of early human anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG promote inflammation by alveolar macrophages

High titers and low fucosylation of early human anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG promote inflammation by alveolar macrophages

High titers and low fucosylation of early human anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG promote inflammation by alveolar macrophages

Transcriptomic similarities and differences in host response between SARS-CoV-2 and other viral infections - ScienceDirect
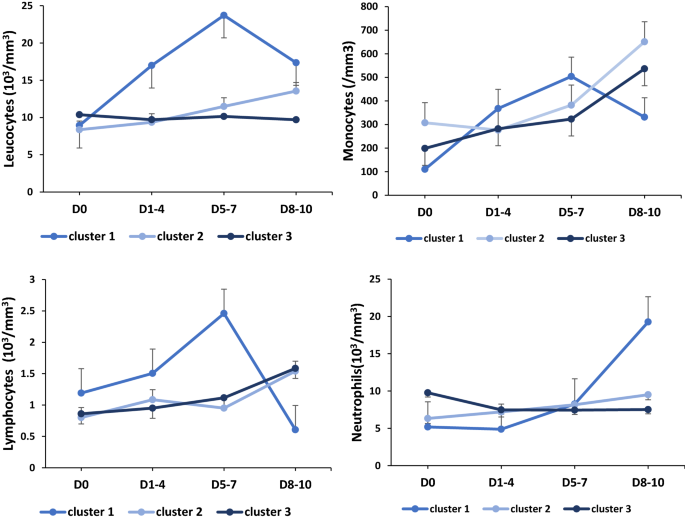
Myeloid phenotypes in severe COVID-19 predict secondary infection and mortality: a pilot study | Annals of Intensive Care | Full Text









